Mastering Risk Assessment in IOSH Managing Safely: A Comprehensive Overview
Risk assessment in IOSH Managing Safely is a pivotal process for professionals in workplace safety management. Whether you’re new to this field or a seasoned practitioner, understanding risk assessment thoroughly is not just critical, but it also empowers you to take control of workplace safety, preparing you for your IOSH Managing Safely certification.
Understanding Risk Assessment in IOSH Managing Safely
A risk assessment involves identifying, evaluating, and addressing potential workplace hazards. It extends beyond mere compliance, aiming to cultivate proactive safety culture.
Why Risk Assessments Matter
Risk assessments are mandated by the Local Govt regulations for workplace health and safety. The risk assessments are essential not only for legal compliance but also for effectively managing and mitigating workplace risks. They are particularly critical for organizations whether small or large, emphasizing the need for a documented safety management approach. A key component of effective risk assessment is compliance with HSE regulations.
When to Conduct Risk Assessments
Regular risk assessments are essential, especially during significant workplace changes, the introduction of new equipment, or in response to near-misses and incidents. Annual reviews are recommended to ensure ongoing safety.
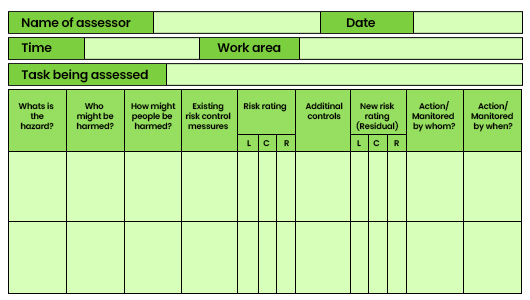
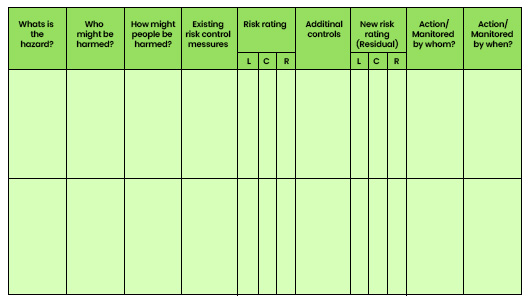
Completing the IOSH Risk Assessment Form
Select a workplace that allows you to identify hazards across categories such as mechanical, physical, chemical, environmental, biological, and organizational.
Hazard Categories in IOSH Managing Safely Syllabus
The course outlines several hazard categories that participants must understand and assess:
1. Mechanical Hazards:
These hazards involve moving machinery parts, equipment malfunctions, or other mechanical issues that can cause harm or injury to individuals working with or around such equipment.
2. Physical Hazards:
Physical hazards include factors like noise, vibration, poor lighting conditions, extreme temperatures, or ergonomic risks. If not managed properly, these hazards can lead to discomfort, injuries, or long-term health issues.
3. Chemical Hazards:
Chemical hazards involve exposure to harmful substances—solids, liquids, or gases. These substances can cause health issues ranging from irritation to severe toxic effects.
4.Environmental Hazards:
Environmental hazards encompass risks related to the workplace environment, such as slippery floors, uneven surfaces, poor air quality, or inadequate ventilation. These hazards can contribute to accidents or health problems.
5. Biological Hazards:
Biological hazards arise from exposure to bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other microorganisms that cause infections or illnesses. Proper handling and hygiene practices mitigate these risks.
6. Organizational Hazards:
Organizational hazards are associated with workplace culture or organizational structure. Examples include high workload, lack of training, poor communication, or inadequate supervision. These factors can impact employee well-being and safety.
Risk Assessment Process in IOSH Managing Safely
The risk assessment process involves systematic steps that are not just important, but they also guide you through the process of identifying, evaluating, and controlling workplace hazards
- 1. Personal Details and Assessment Information:
Begin by documenting personal details, assessment date, time, and specific work area details.
- 2. Identifying Hazards:
Thoroughly identify potential hazards within the workplace across all categories outlined in the syllabus.
- 3. Assessing Who Might Be Harmed:
Consider all individuals who could potentially be affected by the identified hazards, including employees, contractors, visitors, and the public.
- 4. Determining How People Might Be Harmed:
Enumerate the potential injuries or harm that could result from each identified hazard. This step requires a comprehensive understanding of possible consequences.
- 5. Reviewing Existing Risk Control Measures:
Analyse the effectiveness of current risk control measures and identify any gaps that should be filled.
6. Risk Rating:
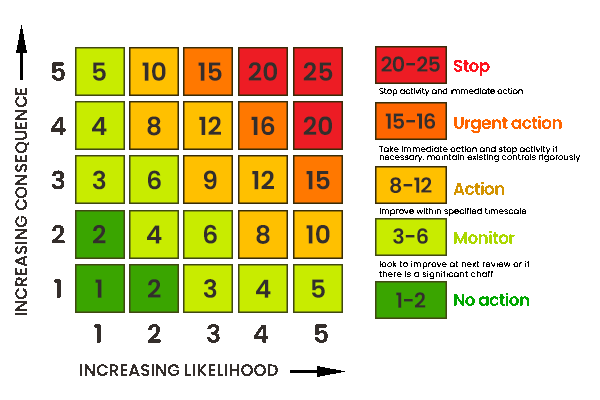
Use a risk rating matrix to assess each identified hazard based on likelihood and consequence. This matrix helps prioritize actions based on the level of risk.
- 7. Implementing Additional Controls:
Develop and implement additional control measures using the control hierarchy (elimination, substitution, engineering controls, administrative controls, personal protective equipment).
- 8. Reassessing Risk After Control Implementation:
Assess the impact of implemented controls on reducing risk levels by conducting a new risk assessment.
- 9. Assigning Responsibilities and Setting Timelines:
Clearly define who is responsible for implementing and monitoring the new control measures and establish realistic timelines for implementation.
- 10. Setting Review Dates:
Plan periodic reviews to assess the effectiveness of implemented measures and to update the risk assessment as necessary.
- 11. Documenting and Closing:
Document all findings, actions taken, responsibilities assigned, and review dates. Ensure proper closure of the risk assessment process.
By following this structured risk assessment process and understanding the various hazard categories outlined in the IOSH Managing Safely syllabus, participants can effectively manage workplace risks and contribute to creating a safer work environment for all. This approach meets regulatory requirements and fosters a proactive safety culture within organizations.
Additional Controls Explained
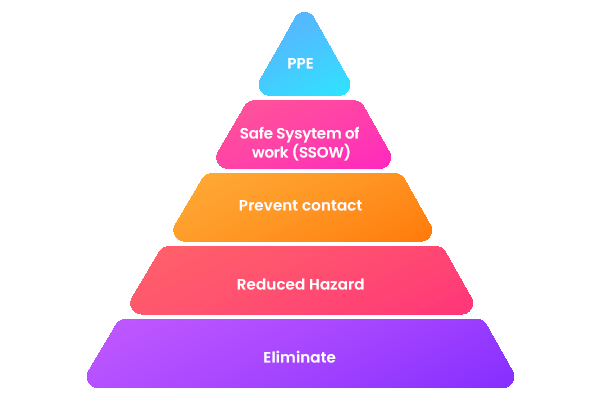
- Eliminate:
The best way to ensure workplace safety is by completely removing the hazard whenever feasible. Although not always possible, elimination remains the most effective solution.
- Reduce Hazard:
If elimination isn’t viable, focus on reducing the hazard’s frequency or intensity. This might involve modifying equipment or refining processes.
- Prevent Contact:
Implement physical barriers like guardrails or locked enclosures to prevent people from encountering hazards directly.
- Safe System of Work (SSOW):
Develop clear, written procedures outlining safe task execution. These may include step-by-step instructions and safety checklists.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
As a final layer of defence, provide appropriate PPE like gloves, safety goggles, or hearing protection to mitigate individual risk.
When considering consequences
- Equipment Adjustments:
Lowering equipment voltage can decrease the risk of severe electric shocks.
- Chemical Substitution:
Use less harmful chemicals to minimize exposure risks.
It’s crucial to maintain some hazards for effective risk assessment. After implementing additional controls, reassess the risk to reflect the reduced level.
Key post-implementation steps include:
- Action Monitoring:
Assign responsibilities to individuals like safety officers or department managers for control implementation.
- Implementation Timeline:
Establish a realistic deadline for new measures, allowing for procurement, training, and adjustments.
- Review and Closing Details:
Schedule a review date to assess control effectiveness. Sign the form and include your training provider’s name, such as Green World Group.
Scoring in IOSH Managing Safely Risk Assessment
To ensure that your assessment is comprehensive and compliant, it is important to understand how each section contributes to your overall score.
| Risk Assessment Section | Marks Available |
|---|---|
| What is the hazard? | 1 |
| Who might be harmed? | 4 |
| Existing Control measures | 4 |
| Risk Rating | 4 |
| Additional Controls | 4 |
| New Risk Rating | 4 |
| Action/monitored by whom? | 4 |
| Action/monitored by when? | 4 |
| Closing Details | 1 |
Selecting the Right Workplace for Assessment
Choose a workplace conducive to identifying diverse hazards, such as mechanical, environmental, and biological risks.
Timeframe to Complete IOSH Risk Assessment
Allocate sufficient time for a thorough assessment. E-learning students typically have a two-week window, while in-person course participants complete it within the standard course duration.
Passing IOSH Managing Safely Course
To pass, you must achieve a minimum of 60 points combined in two assessments:
- 1. Written Assessment:
Score at least 60% (36 points out of 60) in a 30-question test or exam.
- 2. Practical Project:
Conduct a risk assessment focusing on four hazards, scoring at least 23 points (60% of 38).
In cases of near pass, revise the practical project to improve scores.
Conclusion
Mastering IOSH Managing Safely Risk Assessment is pivotal for promoting a safety-conscious workplace culture. Utilize this guide to enhance your understanding of risk management and its application.
Why Choose Green World Group for Safety Course Training
Green World Group stands out for its:
Industry Expertise: Real-world experienced professionals as trainers.
Flexible Learning Modes: Tailored to individual needs.
- Outstanding Support: Unparalleled support from enrollment to certification.
- High Success Rate: Proven efficacy in student exam success.
A wise investment in your future is choosing the right training provider. Not only does it prepare you for your exam, but it also ensures that you are able to apply principles of health and safety to real-life scenarios.






